
Article
7 business telecommunication terms you should know! | Essential Glossary
In the fast-evolving landscape of business mobile phone technology, staying in the loop of key terms and trends is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern workplace. As businesses increasingly embrace digital transformation, understanding terminology becomes essential. So, what are the business mobile terms that professionals should know? In this article, we present seven terms that are not only relevant but also instrumental in shaping the dynamics of business mobile phone usage. From the transformative implications of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) to the cutting-edge advancements in mobile network technology like 5G and the game-changing eSIM technology, we elaborate the importance of each term.
eSIM
An eSIM is a form of SIM card that is embedded directly into a device, eliminating the need for a physical SIM card.
eSIMs are taking mobile connectivity by storm, with an estimated market growth of 16.3 billion USD by 2027, with every major operator supporting the use and sale of eSIMs across the latest handsets. There’s a lot to enjoy from enabling eSIM in work phones, like better flexibility, remote management, and zero-touch provisioning with device management tools.
eSIM, like everything, does have its benefits as well as its drawbacks, and we’ve written a helpful article detailing what eSIM can mean for your business!
READ MORE: eSIM: the latest advance in the world of connectivity for businesses
Bring Your Own Device
BYOD refers to staff using their personal smartphones, tablets, laptops, and desktop PCs to access work servers, work applications and work information, integrating them into a business’s operations.
BYOD is a rising trend in the workplace since the COVID-19 outbreak, where businesses had to adapt to the demands of remote working, filling in gaps an organisation can easily allow collaboration and communication without investing too much in dedicated work devices for its employees. End users of BYOD can enjoy the hassle – free responsibility of only having to worry about a smaller number of devices while still connected to their work ecosystem, bringing about an agile level of flexibility, but like all emerging trends, BYOD poses new challenges and risks that every business should take into consideration. The most glaring threat is lack of security; without the necessary tools and protocols in place, could lead to devasting results like data breaches & leaks, vulnerability to malicious viruses, and violations of intended device usage.
BYOD is a microcosm of two important elements, unified communications bringing everything together into one system, and related device management tools that allow this to happen. There is a plethora of information to gather about BYOD, but we recommend that you visit the official Device Security Guidance from the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre.
“Fleet”
A “fleet” refers to the total number of mobile devices in a business’s inventory used by employees, that are managed collectively.
Line(s)
Refers to telecommunication lines that connect devices or systems for communication purposes.
Mobile Device Management
Mobile Device Management, or MDM, is a process of monitoring, managing, and securing mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets and laptops used in businesses, ensuring that security policies are implemented and followed. MDM has extensive history of the world of telecoms, so here are additional terms that you should know that’s related to MDM:
- Enterprise Mobility Management is an extended approach to MDM that includes the management of mobile software, like installed applications and settings, access to user-specific file storage and content and increased collaboration with enhanced communication tools.
- Unified Endpoint Management is an all-hands approach that covers all endpoints from one access point, like portable laptops, desktop PCs, and Internet of Things devices.
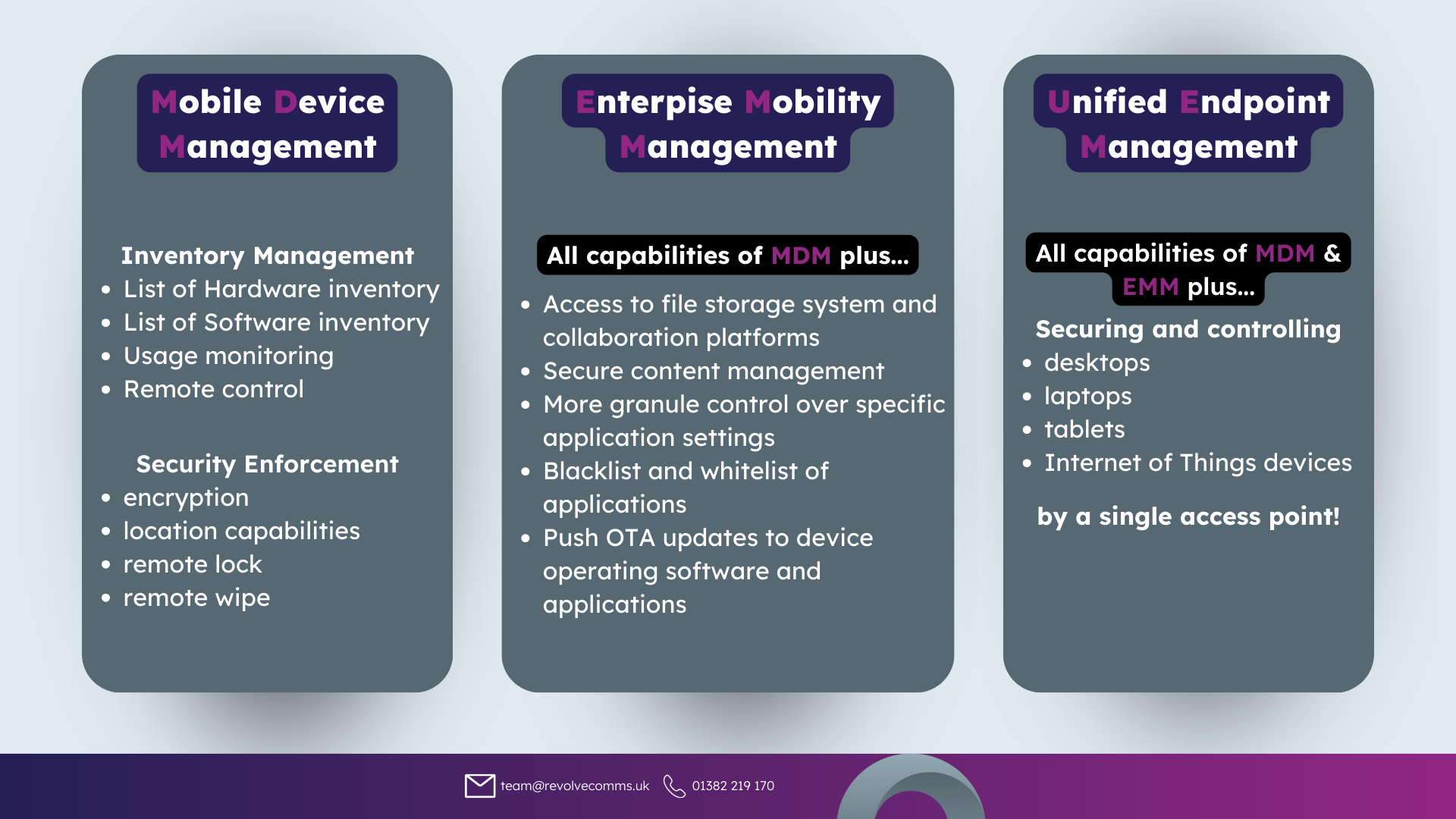
We have an article already covering the world of Unified Endpoint & Device Management, including the reasons why UEM will become more prominent in the work landscape, the core features, and the massive benefits it can bring to a business!
READ MORE: Why businesses should stay in control with Device Management tools
3G, 4G, 5G
3G, 4G, and 5G refer to different generations of mobile network technology, each offering improvements in terms of data speed, capacity, and capabilities.
3G was used for the soaring use of the Internet in the early 2000s that supported the use of multimedia applications like basic browsing, sending & receiving emails, and video calling.
4G: Introduced in the late 2000s, it includes faster data speeds, reaching up to 100 Mbs with improved efficiency.
- Appropriate for high – quality video streaming, high – quality video conferencing, online gaming with very little lag
- + basic internet and connectivity usage with better speed and responsiveness
5G: Introduced in the late 2010s, it includes cutting edge speed of 1,000 Mbs, with very little latency and creating more opportunities for connectivity.
- Appropriate for the highest level of content streaming with 4K & 8K capabilities, IoT Devices connectivity, ultra-low latency
- + basic internet and connectivity usage with the fastest speeds possible.
3G is switching off at the time of writing, so if you’re looking for key dates of when 3G is waning down, as well as a helpful guide on how you can prepare, check out this helpful guide below!
READ MORE: 3G switch-off – Helpful transition guide for businesses in the UK
Business Voice over Internet Protocol
In the context of telecommunications, Voice over Internet Protocol or VoIP, also known as internet telephony, allows you to make phone calls using your broadband connections with your Internet Service Provider, providing an alternative to traditional telephony.
VoIP brings two major benefits for businesses, especially smaller ones: cost savings and the chance of further integration in your business IT ecosystem. VoIP allows you to make calls using your existing internet connection, reducing the amount of spend on calls through your mobile network. Adding VoIP capabilities also means that there lies an opportunity to implement that into a unified setup, where multiple control access points are simplified into one integrated system for ease of use and control. To know more about the bigger picture of unified communications, please read our very own guide of UC, and better understand the world of VoIP here!
READ MORE: How Mobile Network Partners can add to a business’s Unified Communications setup
Conclusion
In conclusion, as the world of business mobile phone technology continues to evolve, a firm grasp of key terms is indispensable for professionals navigating this dynamic landscape. From the paradigm-shifting implications of BYOD to the efficiency gains of VoIP, the comprehensive management strategies of Mobile Device Management, and the transformative potential of 5G and eSIM technology, each term carries its own significance. Businesses that integrate these concepts into their operations stand to gain not only in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness but also in staying ahead of the technological curve. As we move forward, staying informed and adapting to emerging trends will be vital for businesses striving to thrive in the competitive realm of mobile technology.
Revolve Communications is an independent mobile network partner that revolves around your business needs. Gain secure, scalable, and intelligent mobile communications services that enhance your goals.